 栈队列堆
栈队列堆
# 9. 用两个栈实现队列
# 题目链接
牛客网(opens new window) (opens new window)
# 题目描述
用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的 Push 和 Pop 操作。
# 解题思路
in 栈用来处理入栈(push)操作,out 栈用来处理出栈(pop)操作。一个元素进入 in 栈之后,出栈的顺序被反转。当元素要出栈时,需要先进入 out 栈,此时元素出栈顺序再一次被反转,因此出栈顺序就和最开始入栈顺序是相同的,先进入的元素先退出,这就是队列的顺序。
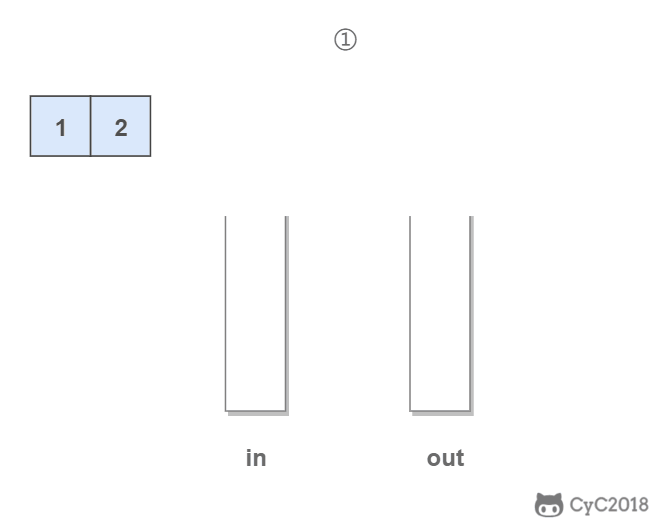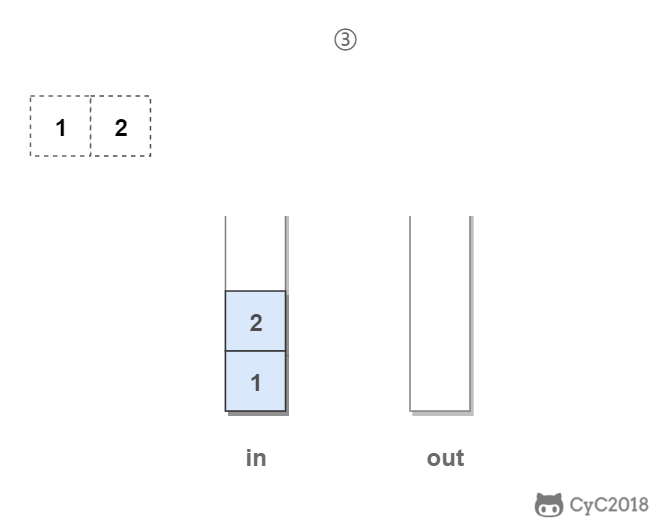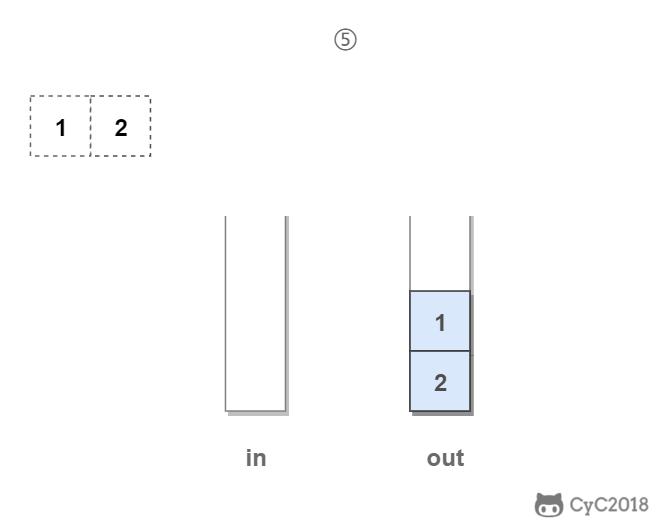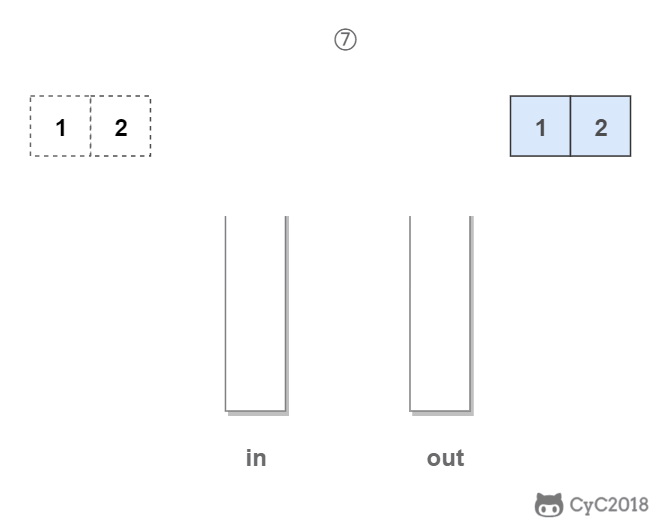
Stack<Integer> in = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> out = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
in.push(node);
}
public int pop() throws Exception {
if (out.isEmpty())
while (!in.isEmpty())
out.push(in.pop());
if (out.isEmpty())
throw new Exception("queue is empty");
return out.pop();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 30. 包含 min 函数的栈
# 题目链接
牛客网(opens new window) (opens new window)
# 题目描述
实现一个包含 min() 函数的栈,该方法返回当前栈中最小的值。
# 解题思路
使用一个额外的 minStack,栈顶元素为当前栈中最小的值。在对栈进行 push 入栈和 pop 出栈操作时,同样需要对 minStack 进行入栈出栈操作,从而使 minStack 栈顶元素一直为当前栈中最小的值。在进行 push 操作时,需要比较入栈元素和当前栈中最小值,将值较小的元素 push 到 minStack 中。
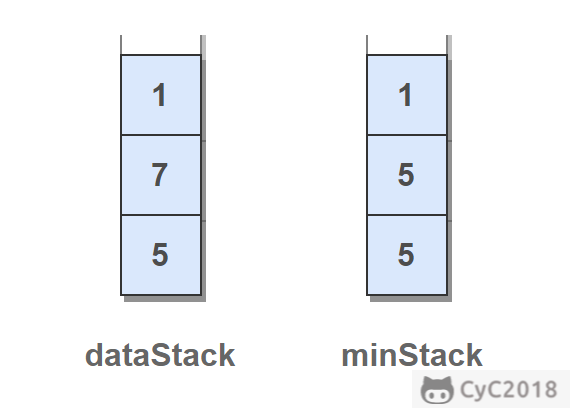
private Stack<Integer> dataStack = new Stack<>();
private Stack<Integer> minStack = new Stack<>();
public void push(int node) {
dataStack.push(node);
minStack.push(minStack.isEmpty() ? node : Math.min(minStack.peek(), node));
}
public void pop() {
dataStack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return dataStack.peek();
}
public int min() {
return minStack.peek();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 31. 栈的压入、弹出序列
# 题目链接
牛客网(opens new window) (opens new window)
# 题目描述
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。
例如序列 1,2,3,4,5 是某栈的压入顺序,序列 4,5,3,2,1 是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但 4,3,5,1,2 就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
# 解题思路
使用一个栈来模拟压入弹出操作。每次入栈一个元素后,都要判断一下栈顶元素是不是当前出栈序列 popSequence 的第一个元素,如果是的话则执行出栈操作并将 popSequence 往后移一位,继续进行判断。
public boolean IsPopOrder(int[] pushSequence, int[] popSequence) {
int n = pushSequence.length;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int pushIndex = 0, popIndex = 0; pushIndex < n; pushIndex++) {
stack.push(pushSequence[pushIndex]);
while (popIndex < n && !stack.isEmpty()
&& stack.peek() == popSequence[popIndex]) {
stack.pop();
popIndex++;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 40. 最小的 K 个数
# 题目链接
牛客网(opens new window) (opens new window)
# 解题思路
# 大小为 K 的最小堆
- 复杂度:O(NlogK) + O(K)
- 特别适合处理海量数据
维护一个大小为 K 的最小堆过程如下:使用大顶堆。在添加一个元素之后,如果大顶堆的大小大于 K,那么将大顶堆的堆顶元素去除,也就是将当前堆中值最大的元素去除,从而使得留在堆中的元素都比被去除的元素来得小。
应该使用大顶堆来维护最小堆,而不能直接创建一个小顶堆并设置一个大小,企图让小顶堆中的元素都是最小元素。
Java 的 PriorityQueue 实现了堆的能力,PriorityQueue 默认是小顶堆,可以在在初始化时使用 Lambda 表达式 (o1, o2) -> o2 - o1 来实现大顶堆。其它语言也有类似的堆数据结构。
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] nums, int k) {
if (k > nums.length || k <= 0)
return new ArrayList<>();
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o2 - o1);
for (int num : nums) {
maxHeap.add(num);
if (maxHeap.size() > k)
maxHeap.poll();
}
return new ArrayList<>(maxHeap);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 快速选择
- 复杂度:O(N) + O(1)
- 只有当允许修改数组元素时才可以使用
快速排序的 partition() 方法,会返回一个整数 j 使得 a[l..j-1] 小于等于 a[j],且 a[j+1..h] 大于等于 a[j],此时 a[j] 就是数组的第 j 大元素。可以利用这个特性找出数组的第 K 个元素,这种找第 K 个元素的算法称为快速选择算法。
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] nums, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (k > nums.length || k <= 0)
return ret;
findKthSmallest(nums, k - 1);
/* findKthSmallest 会改变数组,使得前 k 个数都是最小的 k 个数 */
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
ret.add(nums[i]);
return ret;
}
public void findKthSmallest(int[] nums, int k) {
int l = 0, h = nums.length - 1;
while (l < h) {
int j = partition(nums, l, h);
if (j == k)
break;
if (j > k)
h = j - 1;
else
l = j + 1;
}
}
private int partition(int[] nums, int l, int h) {
int p = nums[l]; /* 切分元素 */
int i = l, j = h + 1;
while (true) {
while (i != h && nums[++i] < p) ;
while (j != l && nums[--j] > p) ;
if (i >= j)
break;
swap(nums, i, j);
}
swap(nums, l, j);
return j;
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int t = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = t;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# 41.1 数据流中的中位数
# 题目链接
牛客网(opens new window) (opens new window)
# 题目描述
如何得到一个数据流中的中位数?如果从数据流中读出奇数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后位于中间的数值。如果从数据流中读出偶数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后中间两个数的平均值。
# 示例1
输入:
[5,2,3,4,1,6,7,0,8]
返回值:
"5.00 3.50 3.00 3.50 3.00 3.50 4.00 3.50 4.00 "
说明:
数据流里面不断吐出的是5,2,3...,则得到的平均数分别为5,(5+2)/2,3...
# 示例2
输入:
[1,1,1]
返回值:
"1.00 1.00 1.00 "
# 解题思路
/* 大顶堆,存储左半边元素 */
private PriorityQueue<Integer> left = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o2 - o1);
/* 小顶堆,存储右半边元素,并且右半边元素都大于左半边 */
private PriorityQueue<Integer> right = new PriorityQueue<>();
/* 当前数据流读入的元素个数 */
private int N = 0;
public void Insert(Integer val) {
/* 插入要保证两个堆存于平衡状态 */
if (N % 2 == 0) {
/* N 为偶数的情况下插入到右半边。
* 因为右半边元素都要大于左半边,但是新插入的元素不一定比左半边元素来的大,
* 因此需要先将元素插入左半边,然后利用左半边为大顶堆的特点,取出堆顶元素即为最大元素,此时插入右半边 */
left.add(val);
right.add(left.poll());
} else {
right.add(val);
left.add(right.poll());
}
N++;
}
public Double GetMedian() {
if (N % 2 == 0)
return (left.peek() + right.peek()) / 2.0;
else
return (double) right.peek();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 41.2 字符流中第一个不重复的字符
# 题目描述
牛客网(opens new window) (opens new window)
# 题目描述
请实现一个函数用来找出字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符。例如,当从字符流中只读出前两个字符 "go" 时,第一个只出现一次的字符是 "g"。当从该字符流中读出前六个字符“google" 时,第一个只出现一次的字符是 "l"。
# 示例1
输入:
"google"
返回值:
"ggg#ll"
# 示例2
"abcdee"
返回值:
"aaaaaa"
# 解题思路
使用统计数组来统计每个字符出现的次数,本题涉及到的字符为都为 ASCII 码,因此使用一个大小为 128 的整型数组就能完成次数统计任务。
使用队列来存储到达的字符,并在每次有新的字符从字符流到达时移除队列头部那些出现次数不再是一次的元素。因为队列是先进先出顺序,因此队列头部的元素为第一次只出现一次的字符。
private int[] cnts = new int[128];
private Queue<Character> queue = new LinkedList<>();
public void Insert(char ch) {
cnts[ch]++;
queue.add(ch);
while (!queue.isEmpty() && cnts[queue.peek()] > 1)
queue.poll();
}
public char FirstAppearingOnce() {
return queue.isEmpty() ? '#' : queue.peek();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 59. 滑动窗口的最大值
# 题目链接
牛客网(opens new window) (opens new window)
# 题目描述
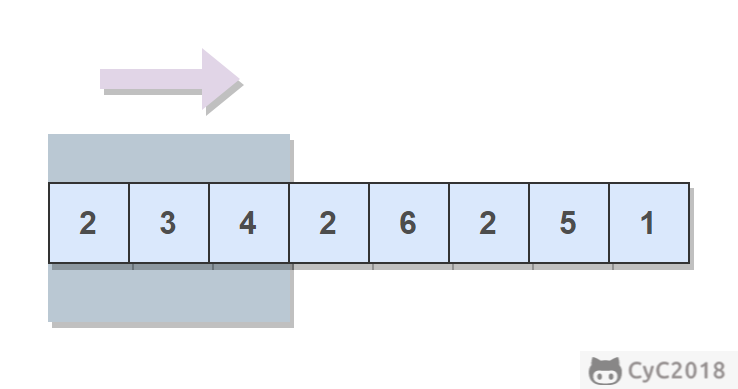
给定一个数组和滑动窗口的大小,找出所有滑动窗口里数值的最大值。
例如,如果输入数组 {2, 3, 4, 2, 6, 2, 5, 1} 及滑动窗口的大小 3,那么一共存在 6 个滑动窗口,他们的最大值分别为 {4, 4, 6, 6, 6, 5}。
# 解题思路
维护一个大小为窗口大小的大顶堆,顶堆元素则为当前窗口的最大值。
假设窗口的大小为 M,数组的长度为 N。在窗口向右移动时,需要先在堆中删除离开窗口的元素,并将新到达的元素添加到堆中,这两个操作的时间复杂度都为 log2M,因此算法的时间复杂度为 O(Nlog2M),空间复杂度为 O(M)。
public ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows(int[] num, int size) {
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (size > num.length || size < 1)
return ret;
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o2 - o1); /* 大顶堆 */
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
heap.add(num[i]);
ret.add(heap.peek());
for (int i = 0, j = i + size; j < num.length; i++, j++) { /* 维护一个大小为 size 的大顶堆 */
heap.remove(num[i]);
heap.add(num[j]);
ret.add(heap.peek());
}
return ret;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
