 链表
链表
# 6. 从尾到头打印链表
# 题目链接
牛客网(opens new window) (opens new window)
# 题目描述
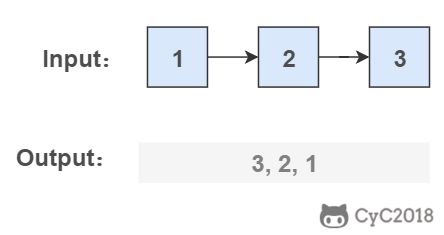
从尾到头反过来打印出每个结点的值。
# 解题思路
# 1. 使用递归
要逆序打印链表 1->2->3(3,2,1),可以先逆序打印链表 2->3(3,2),最后再打印第一个节点 1。而链表 2->3 可以看成一个新的链表,要逆序打印该链表可以继续使用求解函数,也就是在求解函数中调用自己,这就是递归函数。
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (listNode != null) {
ret.addAll(printListFromTailToHead(listNode.next));
ret.add(listNode.val);
}
return ret;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 2. 使用头插法
头插法顾名思义是将节点插入到头部:在遍历原始链表时,将当前节点插入新链表的头部,使其成为第一个节点。
链表的操作需要维护后继关系,例如在某个节点 node1 之后插入一个节点 node2,我们可以通过修改后继关系来实现:
node3 = node1.next;
node2.next = node3;
node1.next = node2;
2
3
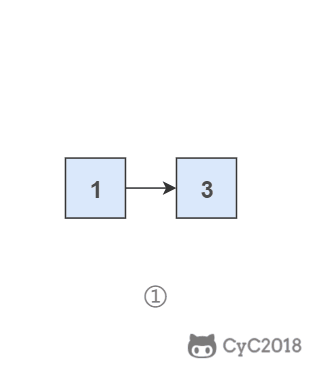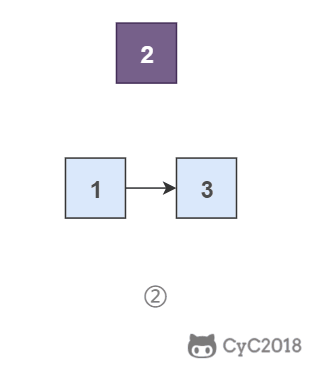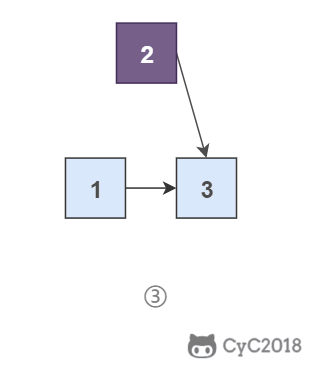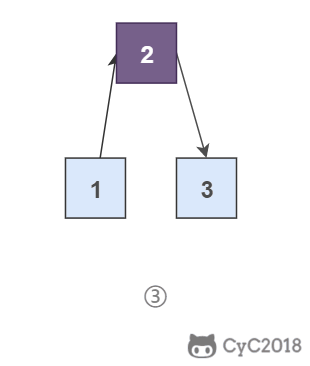
为了能将一个节点插入头部,我们引入了一个叫头结点的辅助节点,该节点不存储值,只是为了方便进行插入操作。不要将头结点与第一个节点混起来,第一个节点是链表中第一个真正存储值的节点。
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
// 头插法构建逆序链表
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
while (listNode != null) {
ListNode memo = listNode.next;
listNode.next = head.next;
head.next = listNode;
listNode = memo;
}
// 构建 ArrayList
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
head = head.next;
while (head != null) {
ret.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
return ret;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
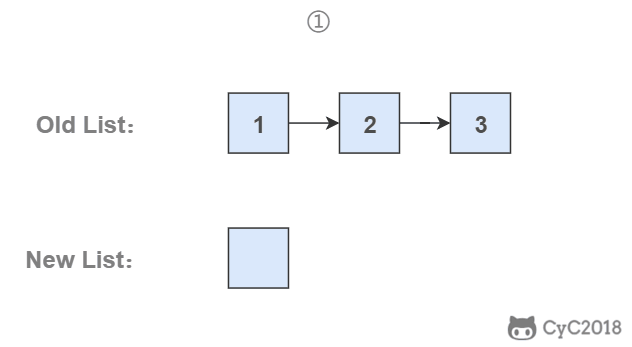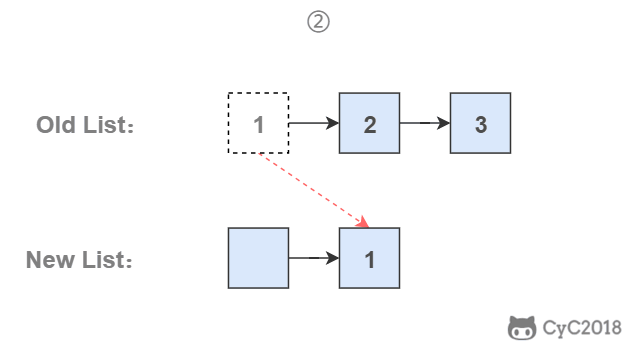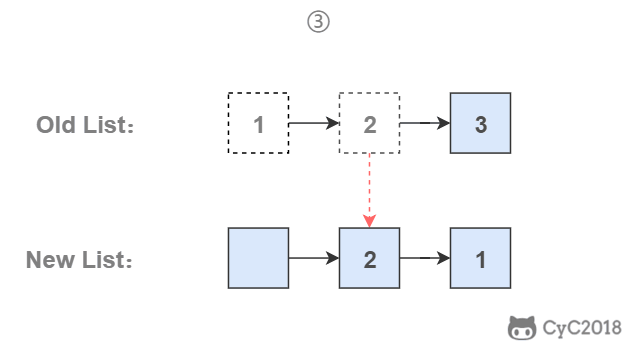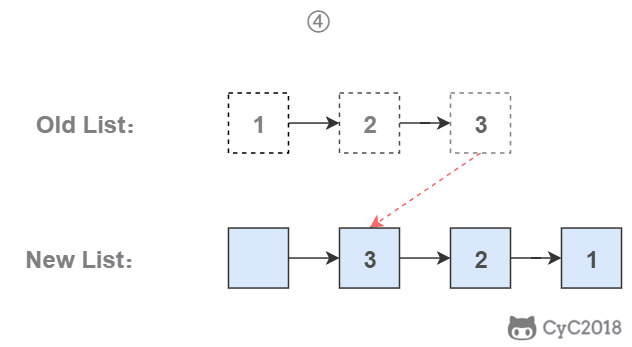
# 3. 使用栈
栈具有后进先出的特点,在遍历链表时将值按顺序放入栈中,最后出栈的顺序即为逆序。
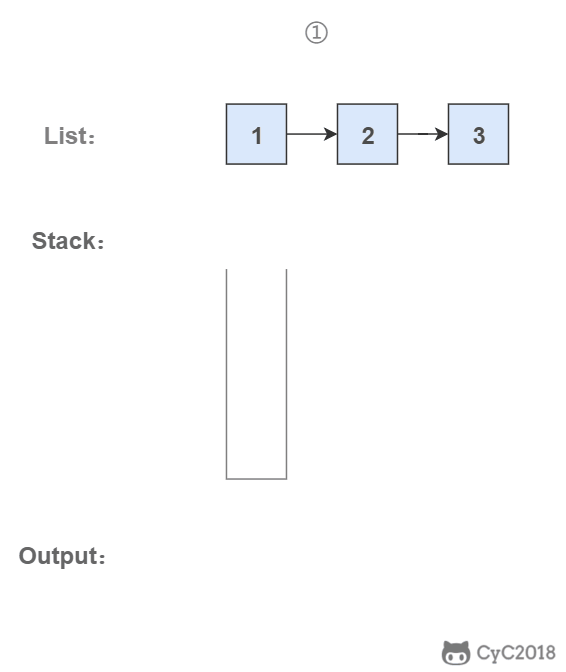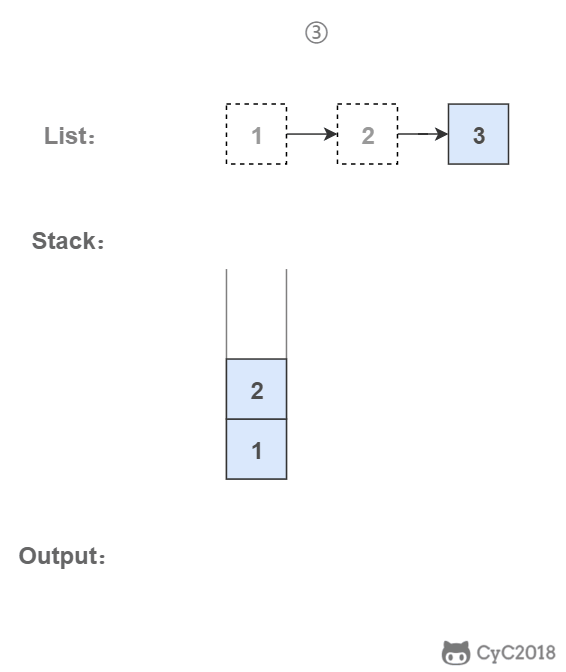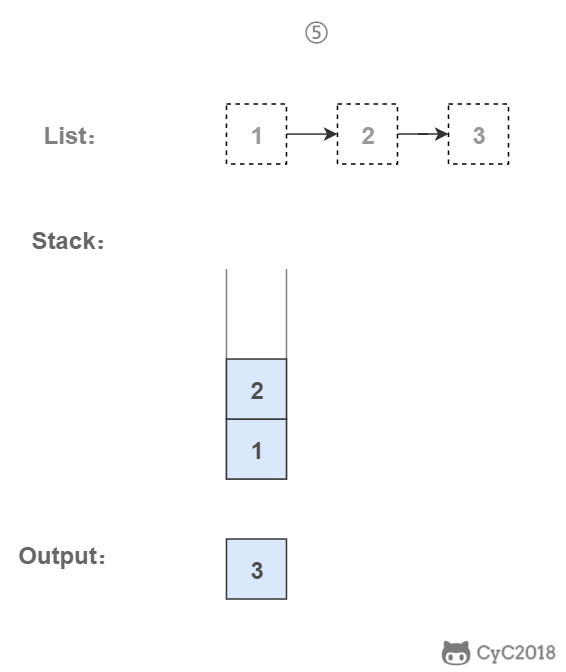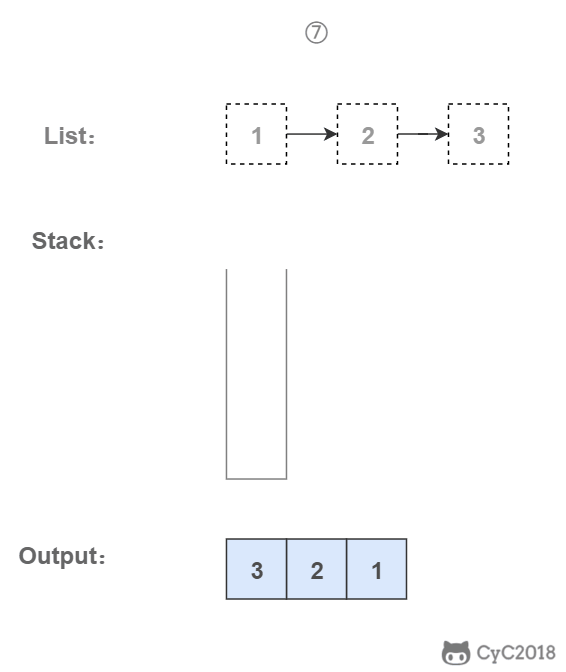
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
while (listNode != null) {
stack.add(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty())
ret.add(stack.pop());
return ret;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 18.2 删除链表中重复的结点
# 题目链接
牛客网(opens new window) (opens new window)
# 题目描述
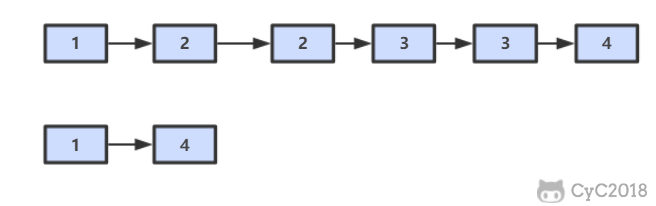
在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。 例如,链表 1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5
# 解题描述
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null)
return pHead;
ListNode next = pHead.next;
if (pHead.val == next.val) {
while (next != null && pHead.val == next.val)
next = next.next;
return deleteDuplication(next);
} else {
pHead.next = deleteDuplication(pHead.next);
return pHead;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 24. 反转链表
NowCoder(opens new window) (opens new window)
# 解题思路
# 递归
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = null;
ListNode newHead = ReverseList(next);
next.next = head;
return newHead;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 迭代
使用头插法。
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode newList = new ListNode(-1);
while (head != null) {
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = newList.next;
newList.next = head;
head = next;
}
return newList.next;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 25. 合并两个排序的链表
NowCoder(opens new window) (opens new window)
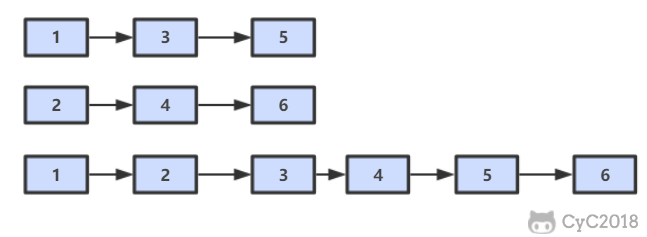
# 题目描述
# 解题思路
# 递归
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null)
return list2;
if (list2 == null)
return list1;
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
list1.next = Merge(list1.next, list2);
return list1;
} else {
list2.next = Merge(list1, list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 迭代
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = head;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
cur.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
cur.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if (list1 != null)
cur.next = list1;
if (list2 != null)
cur.next = list2;
return head.next;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 35. 复杂链表的复制
NowCoder(opens new window) (opens new window)
# 题目描述
输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针指向任意一个节点),返回结果为复制后复杂链表的 head。
public class RandomListNode {
int label;
RandomListNode next = null;
RandomListNode random = null;
RandomListNode(int label) {
this.label = label;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 解题思路
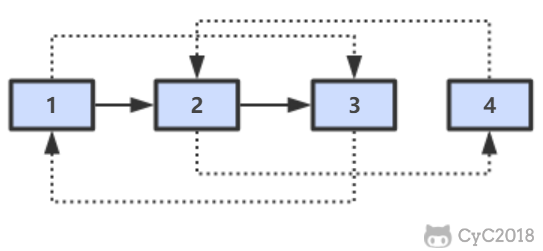
第一步,在每个节点的后面插入复制的节点。
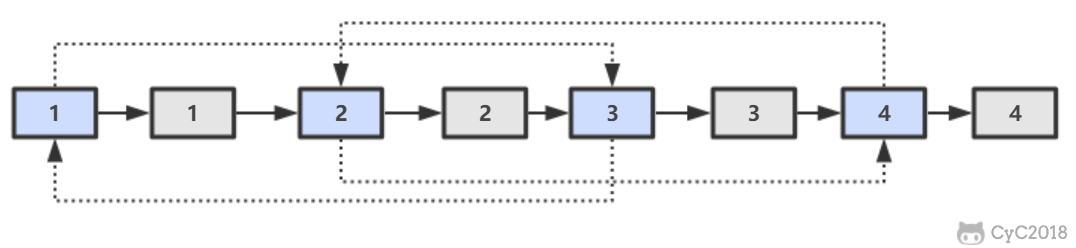
第二步,对复制节点的 random 链接进行赋值。
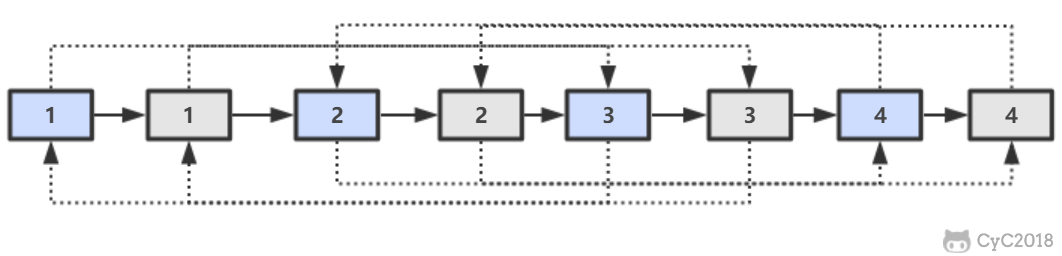
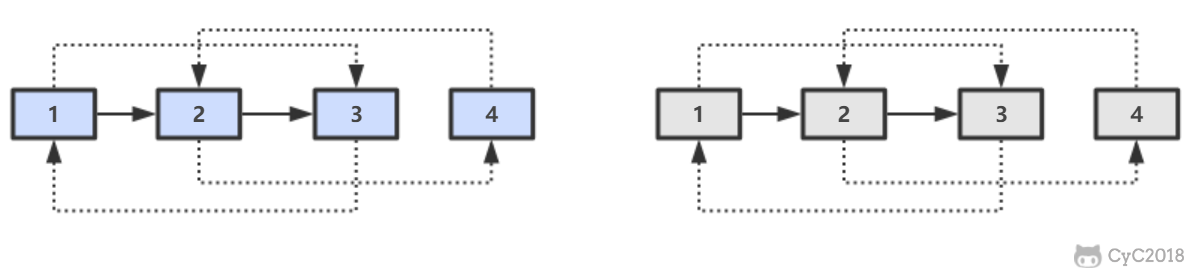
第三步,拆分。
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null)
return null;
// 插入新节点
RandomListNode cur = pHead;
while (cur != null) {
RandomListNode clone = new RandomListNode(cur.label);
clone.next = cur.next;
cur.next = clone;
cur = clone.next;
}
// 建立 random 链接
cur = pHead;
while (cur != null) {
RandomListNode clone = cur.next;
if (cur.random != null)
clone.random = cur.random.next;
cur = clone.next;
}
// 拆分
cur = pHead;
RandomListNode pCloneHead = pHead.next;
while (cur.next != null) {
RandomListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = next.next;
cur = next;
}
return pCloneHead;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 52. 两个链表的第一个公共结点
NowCoder(opens new window) (opens new window)
# 题目描述
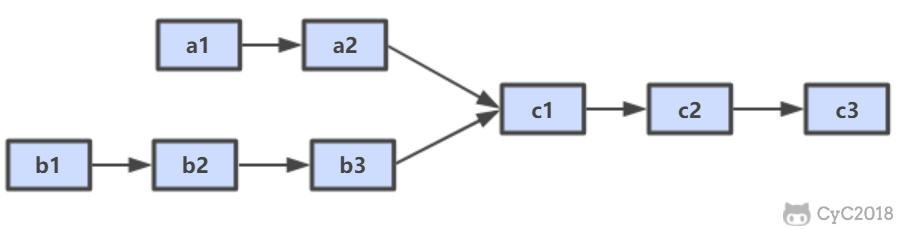
# 解题思路
设 A 的长度为 a + c,B 的长度为 b + c,其中 c 为尾部公共部分长度,可知 a + c + b = b + c + a。
当访问链表 A 的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 B 的头部重新开始访问链表 B;同样地,当访问链表 B 的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 A 的头部重新开始访问链表 A。这样就能控制访问 A 和 B 两个链表的指针能同时访问到交点。
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
ListNode l1 = pHead1, l2 = pHead2;
while (l1 != l2) {
l1 = (l1 == null) ? pHead2 : l1.next;
l2 = (l2 == null) ? pHead1 : l2.next;
}
return l1;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
